Master The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 in 30 mins! 🌟” These”The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Short Notes” is crisp, exam-focused notes break down NCERT’s Chapter 5 “The Fundamental Unit of Life” easy tables and listicles .
The below short notes covers the pure essentials on which the questions are always asked.
And it is also perfect for quick revision and memorization.
After you have finished the preparation of the short notes , Test yourself next! ➡️ Practice MCQs Quiz on the same topic
Discovery Of Cell Study Notes
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Short Study Notes Core Discovery FactsFeature Description Scientist Robert Hooke (1665) 👨🔬 Sample Cork slice (oak bark) 🪵 Tool Self-designed microscope 🔬 Term Origin Latin “cellula” = “little room” 🚪
Key Observations Structure 🧱Saw honeycomb-like compartments 🐝 Named compartments “cells” 🏠 Significance 🌟First evidence: Life = made of separate units ✅ Foundation of Cell Theory 📜 Legacy 🕰️Term “cell” still used in biology today 🔬 All organisms = made of cells Cells = basic functional unit ⚡ | Hooke’s cork = Birth of cell biology! 🎉🔬“Little rooms” → Life’s building blocks! 🧱✨
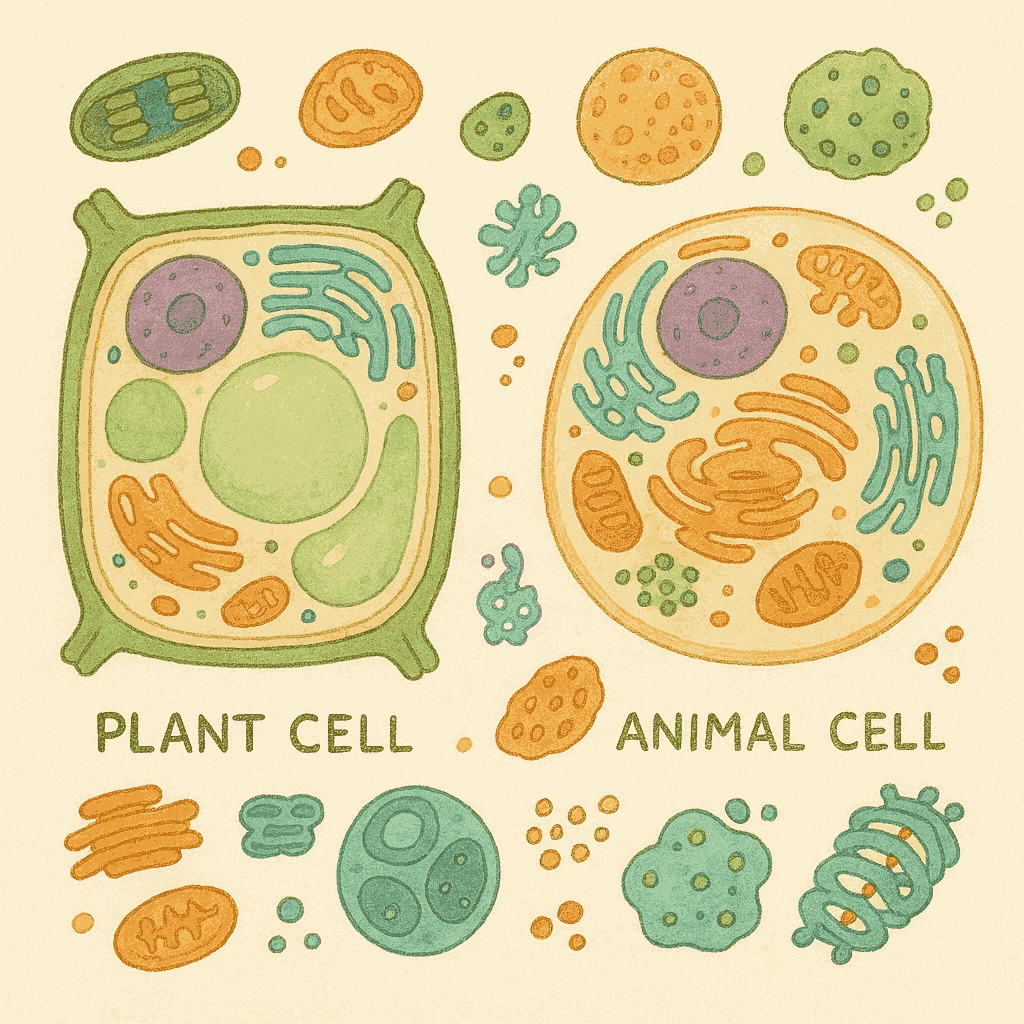
What are Living Organisms Made Up of? Study Notes Cells are the basic building units of all organisms.All organisms (onions, plants, animals) are made of cells. Some single cells live independently (e.g., Amoeba ). Key Discoveries About Cells Year Scientist Discovery 1665 Robert Hooke First observed cells in cork (primitive microscope). 1674 Leeuwenhoek Discovered free-living cells in pond water (improved microscope). 1831 Robert Brown Discovered the nucleus . 1839 Purkinje Coined term “protoplasm” (cell fluid). 1838-39 Schleiden & Schwann Cell Theory : All plants/animals are made of cells; cell = basic unit of life.1855 Virchow Expanded theory: All cells arise from pre-existing cells . 1940 – Electron microscope revealed complex cell structure and organelles .
Cell Characteristics Shape & Size : Related to specific function.Amoeba : Changing shape.Nerve cells: Fixed, peculiar shape. Function : Every living cell performs basic life functions.Division of Labor :Cells contain organelles (specialized components). Each organelle has a specific role (e.g., making materials, clearing waste). Universal Fact : All cells share the same organelles, regardless of function or organism.Core Takeaway Cells are the fundamental units of life, with specialized organelles enabling all functions. Single cells can be entire organisms (e.g., Amoeba ).
What is a Cell Made Up of? What is the Structural Organisation of a Cell? Study notesWhat is a Cell Made Up of? What is the Structural Organisation of a Cell? Organelles (specialized components)Plasma membrane (outer boundary)Enables all cellular activities Nucleus (control center)Interacts with the environment Cytoplasm (fluid matrix)Found in all cells Universal in almost every cell
Key Insights Organelles drive cell functions (e.g., energy production, waste removal).Plasma membrane : Regulates entry/exit of substances.Nucleus : Contains genetic material.Cytoplasm : Houses organelles and facilitates chemical reactions.Together, these 3 features enable all cellular activities and environmental interactions. Plasma Membrane Study Notes Core Functions Feature Description Location Outermost layer 🛡️ Function Separates cell from environment ↔️ Permeability Selectively permeable: allows specific materials in/out ✅🚫
Substance Movement Process Definition Example Diffusion Movement: high → low concentration 📉 CO₂ (out), O₂ (in) 💨 Osmosis Water diffusion → higher solute 🚰 Water balance ⚖️
Osmosis & Solutions Solution Type Water Concentration Cell Effect Hypotonic Higher outside → Cell swells 💧📈 Isotonic Equal inside/outside → No change ↔️ Hypertonic Lower outside → Cell shrinks 💧📉
Key Facts Structure 🧱: Lipids + proteins (flexible).Endocytosis 🍽️: Engulfs food (e.g., Amoeba).Visibility 🔬: Only via electron microscope.Role 🌱: Gas exchange, water/nutrient transport.Diffusion + osmosis = Vital for cell survival! 🔁💧
Cell Wall Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Location Outside plasma membrane 🛡️ Composition Cellulose (complex sugar) 🧪 Function Structural strength + rigidity 💪 Present in Plants 🌿, Fungi 🍄, Bacteria 🦠
Plasmolysis Key Point Effect Cause Water loss via osmosis 💧 Process Cell contents shrink away from wall 📉 Requirement Only in living cells ✅
Hypotonic Solution Response Step Action 1 Cell absorbs water → swells 💦 2 Pressure builds against wall ⚡ 3 Wall exerts equal pressure ↔️ Result Prevents bursting 🛑💥
vs. Animal Cells Advantage Reason Survives dilute media Wall withstands pressure 🛡️ Greater adaptability Handles environmental changes 🌊
Cell wall = Plant’s armor! 🏰🌿
Nucleus Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Location Center of cell 🎯 Covering Double-layered nuclear membrane 🌀 Pores Allow material transfer ↔️ Key Content Chromosomes (DNA + protein) 🧪
DNA & Chromosomes State Structure Function Non-Dividing Cell Chromatin (thread-like mass) 🧵 Stores genetic info 💾 Dividing Cell Chromosomes (rod-shaped) 📏 Inheritance + cell organization 🧬 Genes Functional DNA segments 🧫 Trait transmission 👨👩👧
Staining for Visibility Stain Purpose Observation Iodine Highlights structures 🔦 Uneven coloring (darker regions = nucleus) Safranin/Methylene Blue Cell visualization 👀 Nucleus differentiation 🧫
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Feature Prokaryotes (e.g., Bacteria) 🦠 Eukaryotes 🌿👤 Nuclear Membrane Absent (nucleoid) ❌ Present ✅ DNA Organization Free-floating nucleic acids 🌊 Chromatin/chromosomes 📊 Organelles Absent ❌ Present (mitochondria, plastids) ✅
Functions Cellular Reproduction ➗: Divides to form new cells.Cell Development 📈: Directs chemical activities + maturation.Genetic Control 🎮: Inherits traits via DNA (parents → offspring).Nucleus = Cell’s command center! 💻🧠
Cytoplasm Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Location Inside plasma membrane 🛡️ State Fluid content 💧 Staining Takes little stain 🔬 Composition Water + salts + organelles 🧪
Key Components Element Function Presence Cell Organelles Specialized structures for functions 🧩 Eukaryotes only ✅ Cytosol Gel-like base for reactions ⚗️ All cells 🌐
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Feature Prokaryotes 🦠 Eukaryotes 🌿👤 Organelles Absent ❌ Membrane-bound ✅ Nuclear Region Undefined (nucleoid) 🌫️ Defined nucleus 🧬 Membranes None ❌ Enclose organelles 🌀
Membrane Significance Case Outcome Viruses 🦠No membranes → non-living until host entry ⚠️ Organelles 🧩Membranes enable specialized functions ⚡
Cytoplasm = Cell’s reaction hub! 🔬⚡
Cell Organelles Study Notes Core Function Role Key Point Purpose Separate chemical activities 🧪 Presence Eukaryotes only ✅ Visibility Some need electron microscope 🔬
Organelle Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 🌀Structure : Membrane network (tubes/sheets)Types :Rough ER → Ribosomes → Protein synthesis 🧬 Smooth ER → Lipid synthesis ⚡ Function : Transport highway ↔️Golgi Apparatus 📦Structure : Stacked flattened sacsFunction :Modifies & sorts proteins/lipids ✨ Packages into vesicles 📭 Lysosomes 🧼Structure : Enzyme-filled sacsFunction :Digest waste/cell debris ♻️ Destroy pathogens 🦠 Nickname : “Suicide bags” ⚠️Mitochondria 🔋Structure :Double membrane Inner folds = cristae 📏 Function : ATP production → “Powerhouse” ⚡Plastids 🌿 (Plants only )Types :Chloroplasts → Photosynthesis ☀️ Chromoplasts → Pigments 🌈 Leucoplasts → Storage (starch) 🥔 Eukaryotes vs. Prokaryotes Feature Eukaryotes ✅ Prokaryotes ❌ Membrane-bound organelles Present 🏭 Absent Nucleus Enclosed 🧬 Nucleoid Complexity High (e.g., plants/animals) 🌳 Low (bacteria) 🦠
Organelles = Cell’s specialized factories! 🏭⚙️
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Structure Membrane-bound tubes & sheets 🛤️ Appearance Tubules or vesicles (bags) 🔍 Membrane Similar to plasma membrane 🛡️ Types RER (rough) & SER (smooth) ↔️
ER Types Rough ER (RER) 📏Surface : Ribosome-covered → rough texture 🧫Function : Protein synthesis 🧬Transport : Sends proteins to cell destinations 📭Smooth ER (SER) ⚡Surface : No ribosomes → smooth 🔬Function :Lipid/fat synthesis ⚗️ Membrane biogenesis 🏗️ Liver cells : Detoxifies poisons/drugs 🧴Key Functions Role Mechanism Transport Highway ↔️Moves proteins between cytoplasm & nucleus Framework 🖼️Supports biochemical reactions Membrane Builder 🧱Creates cell membrane via lipids/proteins Hormone/Enzyme Factory 🏭Produces signaling molecules
ER = Cell’s transport & synthesis network! 🚚🏭
Golgi Apparatus Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Discoverer Camillo Golgi (1898) 👨🔬 Structure Stacked membrane sacs (cisternae) 📚 Connection Linked to ER membranes ↔️
Function Packaging Hub 📭Receives materials from ER 🚚 Dispatches to targets (inside/outside cell) 🎯 Modification Station ✨Alters protein/lipid structures 🧬 Synthesizes complex sugars 🍬 → simple sugars Storage & Sorting 🗃️Temporarily stores products ⏳ Sorts materials into vesicles 📦 Lysosome Factory 🧼Forms lysosomes (digestive organelles) ⚙️ Key Process Flow Step Action 1. Receive Collects synthesized material from ER 🚚 2. Process Modifies & packages products ✨📦 3. Dispatch Sends vesicles to destinations 📭
Golgi = Cell’s post office & assembly line! 📬🏭
Lysosomes Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Structure Membrane-bound enzyme sacs 🎒 Enzyme Source Made by RER 🏭 Nickname “Suicide bags” ⚠️
Function Waste Disposal ♻️Digests worn-out organelles 🔄 Breaks down foreign materials (bacteria/food) 🦠🍎 Cellular Cleanup 🧹Releases enzymes → breaks complex → simple substances ⚗️ Maintains internal hygiene ✨ Emergency Response 🚨If cell damaged: bursts + digests own cell 💥(Autolysis = “self-destruction”) Digestion Process Target Action Foreign Invaders 🦠Engulfs bacteria → enzyme breakdown 🔬 Organic Debris 🗑️Recycles damaged cell parts 🔄 Food Particles 🍎Converts nutrients → usable forms ⚡
Lysosomes = Cell’s recycling center & self-destruct system! ♻️💣
Mitochondria Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Nickname “Powerhouse of the cell” ⚡ Membranes Double layer:Outer : Porous 🕳️Inner : Folded (cristae) 📏 Energy Output ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) 💥
Function ATP Production ⚡Converts food → chemical energy 🔥 Fuels cellular activities (growth/repair) 🛠️ Surface Area Boost 📈Inner folds (cristae) → maximize reaction space ⚗️ Self-Replication 🔄Contains own DNA & ribosomes 🧬 Synthesizes some proteins 🧪 ATP = Energy Currency Role Action Chemical Work 🧫Builds new compounds ↔️ Mechanical Work 🏋️Powers muscle contraction 💪
Mitochondria = Cell’s battery + protein factory! 🔋🏭
Plastids Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Presence Only in plant cells 🌱 Types Chromoplasts (colored) & Leucoplasts (colorless) ↔️ DNA/Ribosomes Own genetic material 🧬 (like mitochondria)
Plastid Types Chloroplasts 🟢Pigment : ChlorophyllFunction : Photosynthesis ☀️ → foodExtras : Yellow/orange pigments 🌈Chromoplasts 🎨Pigments : Non-green colors (red/yellow)Function : Attract pollinators 🦋Leucoplasts ⚪Chloroplast Structure Part Description Stroma Gel-like matrix ⚗️ Thylakoids Membrane stacks (pigment layers) 📚 Similarity Double membrane (like mitochondria) 🌀
Plastids = Plant cell’s kitchen & pantry! 👩🍳📦
Vacuoles Study Notes Core Facts Feature Description Function Storage sacs (solid/liquid) 🧴 Animal Cells Small vacuoles 🐭 Plant Cells Large central vacuole (50-90% cell volume) 🌱
Function Storage Hub 📦Holds nutrients, water, waste 🥗💧🗑️ Plant Support 💪Maintains turgor pressure → cell rigidity 📏 Waste Management ♻️Isolates harmful substances ☣️ Cell Organization & Role Respiration 💨 Nutrition 🥗 Waste clearance 🗑️ Protein synthesis 🧬 |Fundamental Unit 🔬 | Structural basis 🏗️ Functional basis ⚡ | Vacuoles = Cell’s storage warehouse! 🏭📦Cells = Life’s building blocks! 🧱💡
Cell Division Study Notes Core Purpose Reason Outcome Growth 📈Increases organism size Repair 🛠️Replaces damaged/dead cells Reproduction 👶Forms gametes (via meiosis)
Types Mitosis ⚖️Function : Growth & tissue repair 🌱Process :1 mother cell → 2 identical daughter cells 🔄 Chromosomes: Same number as mother 🧬 Location : All body cells (except reproductive)Meiosis ✂️Function : Gamete formation (sperm/egg) 🥚Process :1 mother cell → 4 daughter cells 🔄 Chromosomes : Half the mother’s number (Why? 👇)Two divisions (Meiosis I & II) ↔️ Location : Reproductive organs onlyMeiosis Chromosome Halving Step Reason 1. Fertilization 🧬Gametes fuse → restore full chromosome set 2. Genetic Diversity 🧩Ensures species stability across generations 🔁
Mitosis vs. Meiosis Feature Mitosis ✅ Meiosis ✅ Daughter Cells 2 4 Chromosomes Same as mother Half of mother Function Growth/Repair Reproduction Divisions 1 2
Mitosis = Clone factory! 🏭Meiosis = Diversity engine! 🧬✨
Conclusion:The Fundamental Unit Of Life Class 9 Short Notes You’ve Mastered Life’s Blueprint! 🌟You just unlocked the secret code of life ! 🧬✨ From Hooke’s cork cells to mitosis magic , you now see:
Every organism = cells working together 🤝Organelles = specialized factories 🏭Division = growth & renewal 🔄Remember:
“You didn’t just study cells — you discovered how life ticks.” ⏱️💡Go shine! 🚀





Leave a Comment