”MCQs Light Reflection And Refraction Class 10” is based on the NCERT science class 10 Chapter 9: Light – Reflection and Refraction.
For your CBSE preparation, your NCERT textbook is your most trusted map. It lays everything out clearly, step by step, and the board paper follows its path closely. Make sure you’ve gone through every diagram, example, and in-text question.
Our short notes are here to help after you’ve read the chapter.
They’re your quick cheat sheet—perfect for last-minute revision to jog your memory on laws, formulas, and key differences.
We have listed all the questions with answers in this MCQ quiz at the end for your reference.
Good luck with your quiz!
Test your understanding and find areas to improve.
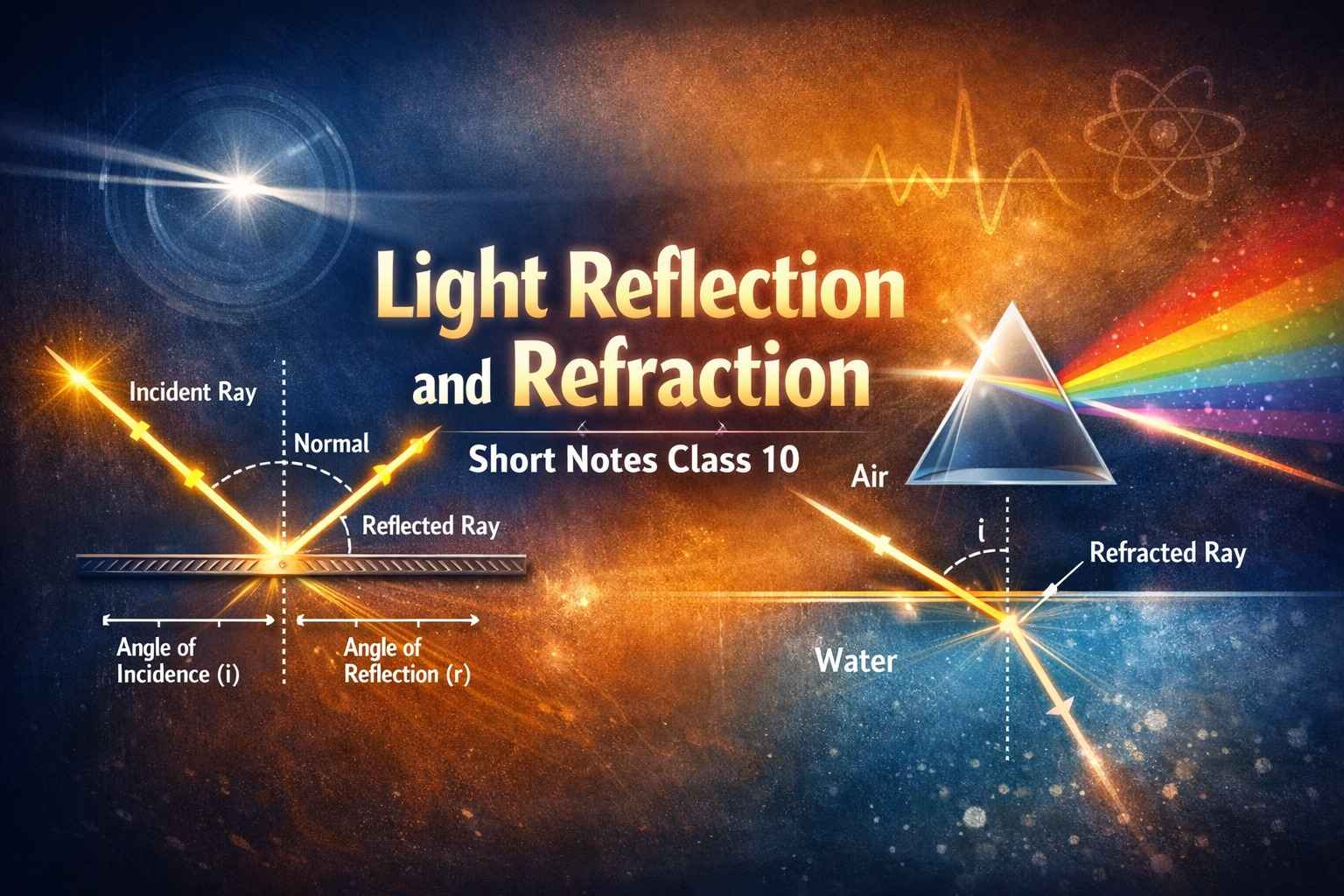
REFLECTION OF LIGHT
SPHERICAL MIRRORS
Image Formation by Spherical Mirrors
Representation of Images Formed by Spherical
Mirrors Using Ray Diagrams
Mirror Formula and Magnification
REFRACTION OF LIGHT
Refraction through a Rectangular Glass Slab
The Refractive Index
Refraction by Spherical Lenses
Image Formation by Lenses
Image Formation in Lenses Using Ray Diagrams
Lens Formula and Magnification
Power of a Lens
Conclusion: MCQs Light Reflection And Refraction Class 10
Great work on finishing the Light quiz! Whether you aced it or stumbled on a few questions, this was a valuable check-in. Each question you get right proves you’re on track, and every mistake is just a spotlight showing you what to review.
Your Next Steps:
- First, go back to your NCERT textbook. Re-read the sections related to any tricky questions.
- Then, use our short notes to solidify those concepts in your mind before your final revision.
All the MCQs Of The Quiz
A highly polished surface that reflects most of the light falling on it is called:
A) Rough surface
B) Mirror
C) Prism
D) Lens
Answer: B
The angle of reflection is always equal to:
A) Angle of deviation
B) Angle of refraction
C) Angle of incidence
D) Angle of scattering
Answer: C
The incident ray, reflected ray and normal at the point of incidence lie:
A) At right angles
B) In different planes
C) In the same plane
D) Along the surface
Answer: C
The image formed by a plane mirror is always:
A) Real and inverted
B) Virtual and erect
C) Real and erect
D) Diminished
Answer: B
The distance between an object and its image in a plane mirror when the object is 4 m away from the mirror is:
A) 2 m
B) 4 m
C) 6 m
D) 8 m
Answer: D
A spherical mirror whose reflecting surface is curved inward is called:
A) Convex mirror
B) Plane mirror
C) Concave mirror
D) Cylindrical mirror
Answer: C
The centre of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is known as:
A) Focus
B) Pole
C) Aperture
D) Axis
Answer: B
The radius of curvature of a mirror is 30 cm. Its focal length is:
A) 10 cm
B) 15 cm
C) 30 cm
D) 60 cm
Answer: B
Which mirror is used as rear-view mirror in vehicles?
A) Plane mirror
B) Concave mirror
C) Convex mirror
D) Parabolic mirror
Answer: C
A concave mirror can form a virtual and erect image when the object is placed:
A) At infinity
B) At C
C) Beyond C
D) Between pole and focus
Answer: D
The mirror formula for spherical mirrors is:
A) 1/v − 1/u = 1/f
B) 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
C) v/u = f
D) f = uv
Answer: B
If magnification for a mirror is negative, the image is:
A) Virtual
B) Real and inverted
C) Erect
D) Same size
Answer: B
When light passes obliquely from one transparent medium to another, it changes direction due to:
A) Reflection
B) Dispersion
C) Refraction
D) Diffraction
Answer: C
A ray entering from air to glass bends:
A) Away from normal
B) Towards normal
C) Parallel
D) Backward
Answer: B
The emergent ray from a rectangular glass slab is:
A) Perpendicular to incident ray
B) Parallel to incident ray
C) Diverging
D) Converging
Answer: B
The ratio sin i / sin r is constant according to:
A) Law of reflection
B) Law of refraction
C) Snell’s law
D) Law of dispersion
Answer: C
The refractive index of a medium is defined as:
A) v/c
B) c/v
C) v1/v2
D) sin r/sin i
Answer: B
If the speed of light in a medium is 2 × 10⁸ m/s, its refractive index is:
A) 1.2
B) 1.33
C) 1.5
D) 2
Answer: C
A convex lens is thicker:
A) At edges
B) At centre
C) Uniformly
D) At one side only
Answer: B
A concave lens is also called:
A) Converging lens
B) Reflecting lens
C) Diverging lens
D) Cylindrical lens
Answer: C
A ray passing through the optical centre of a thin lens:
A) Deviates completely
B) Passes undeviated
C) Reflects back
D) Stops
Answer: B
When an object is placed at infinity in front of a convex lens, the image is formed:
A) At optical centre
B) At 2F
C) At focus
D) At infinity
Answer: C
The lens formula is given by:
A) 1/v + 1/u = 1/f
B) 1/v − 1/u = 1/f
C) v/u = f
D) f = u − v
Answer: B
If the magnification of a lens is +2, the image is:
A) Real and inverted
B) Virtual and erect
C) Same size
D) Diminished
Answer: B
The power of a lens is defined as:
A) f
B) 1/f
C) uv
D) v/u
Answer: B
The SI unit of power of a lens is:
A) Metre
B) Watt
C) Dioptre
D) Hertz
Answer: C
The power of a concave lens is always:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Zero
D) Infinite
Answer: B
A lens of power +2 D has focal length:
A) 0.25 m
B) 0.5 m
C) 2 m
D) 1 m
Answer: B
A lens of focal length 25 cm has power:
A) +2 D
B) +4 D
C) −2 D
D) −4 D
Answer: B
Higher power of a lens means:
A) Longer focal length
B) Lower bending
C) Greater convergence or divergence
D) No refraction
Answer: C
A ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror after reflection passes through:
A) Pole
B) Centre of curvature
C) Principal focus
D) Infinity
Answer: C
A ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror after reflection will:
A) Bend towards focus
B) Emerge parallel
C) Retrace its path
D) Scatter
Answer: C
The diameter of the reflecting surface of a spherical mirror is called:
A) Radius of curvature
B) Aperture
C) Principal axis
D) Focus
Answer: B
For spherical mirrors of small aperture, the relation between radius of curvature and focal length is:
A) R = f
B) R = 4f
C) R = 2f
D) f = 4R
Answer: C
When an object is placed between F and C of a concave mirror, the image formed is:
A) Virtual and erect
B) Real and enlarged
C) Real and diminished
D) Same size
Answer: B
When an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, the image is formed:
A) At C
B) At pole
C) At infinity
D) Between F and C
Answer: C
The magnification produced by a spherical mirror is given by:
A) u/v
B) v/u
C) −v/u
D) f/u
Answer: C
If magnification is +1 in a mirror, the image is:
A) Real and inverted
B) Virtual and erect
C) Highly diminished
D) At infinity
Answer: B
The apparent raising of the bottom of a pond is due to:
A) Reflection
B) Refraction
C) Dispersion
D) Diffraction
Answer: B
When light travels from glass to air, it bends:
A) Towards the normal
B) Away from the normal
C) Along the normal
D) Stops
Answer: B
The sideways shift of light through a glass slab is called:
A) Reflection
B) Lateral displacement
C) Diffraction
D) Dispersion
Answer: B
If a ray is incident normally on a glass slab, it will:
A) Bend towards normal
B) Bend away
C) Reflect
D) Pass without deviation
Answer: D
The refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is given by:
A) v₂/v₁
B) v₁/v₂
C) sin r/sin i
D) c/v₁
Answer: B
Light travels fastest in:
A) Water
B) Glass
C) Vacuum
D) Diamond
Answer: C
If the refractive index of a medium increases, the speed of light in that medium:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains same
D) Becomes infinite
Answer: B
A convex lens converges parallel rays to a point called:
A) Pole
B) Aperture
C) Principal focus
D) Centre of curvature
Answer: C
A concave lens makes parallel rays:
A) Converge
B) Diverge
C) Reflect
D) Stop
Answer: B
The two points on the principal axis where parallel rays meet or appear to meet after refraction are called:
A) Poles
B) Optical centres
C) Principal foci
D) Apertures
Answer: C
The distance between the optical centre and the principal focus of a lens is called:
A) Aperture
B) Radius
C) Focal length
D) Curvature
Answer: C
A concave lens always forms images that are:
A) Real and inverted
B) Real and magnified
C) Virtual and erect
D) Same size
Answer: C
When an object is placed beyond 2F of a convex lens, the image is:
A) Enlarged and virtual
B) Diminished and real
C) Same size
D) At infinity
Answer: B
When an object is placed at 2F of a convex lens, the image is:
A) Same size and real
B) Enlarged and real
C) Virtual
D) Diminished
Answer: A
For a convex lens, placing the object inside the focal length produces an image that is:
A) Real and inverted
B) Virtual and erect
C) Real and diminished
D) Point-sized
Answer: B
The magnification produced by a lens is defined as:
A) h/h′
B) v/u
C) h′/h
D) f/v
Answer: C
The relation between magnification and distances for a lens is:
A) m = −v/u
B) m = v/u
C) m = u/v
D) m = f/u
Answer: B
If image distance equals object distance in magnitude for a convex lens, the object is placed at:
A) Focus
B) Optical centre
C) 2F
D) Infinity
Answer: C
A lens that has focal length 1 m has power:
A) 0.5 D
B) 1 D
C) 2 D
D) 10 D
Answer: B
If a lens has power −2.5 D, it is:
A) Convex
B) Plane
C) Concave
D) Cylindrical
Answer: C
A higher positive power lens has:
A) Longer focal length
B) Smaller focal length
C) No focal length
D) Infinite focal length
Answer: B
The ability of a lens to converge or diverge light rays is measured by its:
A) Aperture
B) Radius
C) Power
D) Diameter
Answer: C
A ray of light directed towards the principal focus of a convex lens, after refraction, will:
A) Pass through the optical centre
B) Emerge parallel to the principal axis
C) Retrace its path
D) Converge at 2F
Answer: B
A ray directed towards the principal focus of a concave lens, after refraction, will:
A) Converge at focus
B) Emerge parallel to the principal axis
C) Pass undeviated
D) Reflect back
Answer: B
To locate the image in a ray diagram for a lens, the minimum number of rays required is:
A) One
B) Two
C) Three
D) Infinite
Answer: B
If the refracted rays from a lens actually meet at a point, the image formed is:
A) Virtual
B) Erect
C) Real
D) Magnified
Answer: C
If refracted rays appear to meet when extended backward, the image is:
A) Real
B) Virtual
C) Same size
D) At infinity
Answer: B
Which lens is used by watchmakers to observe tiny parts clearly?
A) Concave lens
B) Plane mirror
C) Convex lens
D) Glass slab
Answer: C
A convex lens used in a solar furnace concentrates sunlight because it:
A) Reflects rays
B) Diverges rays
C) Converges parallel rays
D) Absorbs heat
Answer: C
If the aperture of a lens is increased, it mainly affects:
A) Focal length
B) Refractive index
C) Amount of light entering
D) Power only
Answer: C
In the Cartesian sign convention for lenses, object distance is generally taken as:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Zero
D) Infinite
Answer: B
For a concave lens, the focal length is considered:
A) Positive
B) Negative
C) Zero
D) Infinite
Answer: B
If an image formed by a lens is inverted, the image must be:
A) Virtual
B) Real
C) Erect
D) Point-sized
Answer: B
A convex lens forms an image at infinity when the object is placed:
A) At 2F
B) At optical centre
C) At focus
D) Beyond 2F
Answer: C
The optical centre of a lens is the point through which a ray:
A) Deviates maximum
B) Reflects
C) Passes undeviated
D) Splits
Answer: C
If the speed of light in two media is the same, the refractive index between them is:
A) Zero
B) One
C) Greater than one
D) Infinite
Answer: B
If refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is less than 1, medium 2 is:
A) Denser
B) Rarer
C) Opaque
D) Reflective
Answer: B
When light travels from vacuum into glass, its frequency:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains same
D) Becomes zero
Answer: C
When light enters a denser medium obliquely, the wavelength:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains same
D) Becomes infinite
Answer: B
A ray parallel to the principal axis incident on a concave lens appears to diverge from:
A) Optical centre
B) Centre of curvature
C) Principal focus
D) Infinity
Answer: C
The point where refracted rays from a convex lens actually meet is called:
A) Pole
B) Principal focus
C) Aperture
D) Radius
Answer: B
Which of the following devices uses both refraction and convergence of light?
A) Plane mirror
B) Periscope
C) Magnifying glass
D) Kaleidoscope
Answer: C
- If the focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm, its power is:
A) +2 D
B) +4 D
C) −4 D
D) −2 D
Answer: B - A lens of power −5 D has focal length:
A) +0.2 m
B) −0.2 m
C) +5 m
D) −5 m
Answer: B - The power of a lens whose focal length is 2 m is:
A) 0.5 D
B) 2 D
C) 4 D
D) −2 D
Answer: A - If two convex lenses of powers +2 D and +3 D are used separately, which one converges light more strongly?
A) +2 D
B) +3 D
C) Both same
D) Neither
Answer: B - A lens with focal length 0.1 m has power:
A) 1 D
B) 5 D
C) 10 D
D) 0.1 D
Answer: C - If the power of a lens is doubled, its focal length becomes:
A) Doubled
B) Halved
C) Four times
D) Unchanged
Answer: B - A concave lens of focal length 50 cm has power:
A) +2 D
B) −2 D
C) +0.5 D
D) −0.5 D
Answer: B - A ray of light passing through the focus of a convex lens before refraction will, after refraction:
A) Pass through optical centre
B) Emerge parallel to principal axis
C) Retrace path
D) Converge at 2F
Answer: B - When parallel rays pass through a concave lens, they:
A) Meet at focus
B) Pass undeviated
C) Appear to diverge from focus
D) Reflect back
Answer: C - Which of the following always produces diminished images for all object positions?
A) Convex lens
B) Plane mirror
C) Concave mirror
D) Concave lens
Answer: D - If the magnification of a lens is greater than 1, the image is:
A) Diminished
B) Same size
C) Enlarged
D) Virtual only
Answer: C - If magnification is positive for a lens, the image is:
A) Real
B) Inverted
C) Virtual and erect
D) At infinity
Answer: C - A real image formed by a convex lens is always:
A) Erect
B) Inverted
C) Virtual
D) Same size
Answer: B - The image formed by a concave lens is always located:
A) Beyond 2F
B) At focus on opposite side
C) Between focus and optical centre on same side
D) At infinity
Answer: C - For a convex lens, if the object distance is equal to twice the focal length, the image distance will be:
A) f
B) 2f
C) f/2
D) Infinity
Answer: B - A student observes that the image formed by a lens cannot be caught on a screen. The image must be:
A) Real
B) Inverted
C) Virtual
D) Same size
Answer: C - The bending of light through a lens occurs due to:
A) Reflection
B) Diffraction
C) Change in speed in different media
D) Absorption
Answer: C - If the refractive index of glass increases, the focal length of a convex lens generally:
A) Increases
B) Decreases
C) Remains same
D) Becomes zero
Answer: B - A ray diagram helps to determine the nature, position, and size of the image formed by:
A) Mirrors only
B) Lenses only
C) Both mirrors and lenses
D) Prisms only
Answer: C - The quantity that measures the degree of convergence or divergence of a lens is called its:
A) Radius
B) Aperture
C) Power
D) Axis
Answer: C




