
🎯 Unlock India’s Rulebook: Constitutional Design Class 9 Made Simple!
Ever wondered who controls the controllers? 🤔 What stops leaders from becoming dictators? Why can’t a state ban your favorite festival?
The secret lies in India’s constitutional design – the ultimate “game rules” that turn democracy from a dream into reality.
For Class 9 students, this isn’t just a chapter – it’s your power manual. You’ll discover:
🔥 How freedom fighters’ values became enforceable rules (like Gandhi’s dream of equality!).
⚡️ Why South Africa’s anti-apartheid struggle holds the key to understanding India’s system.
💡 Shocking truths about the “contradictions” Dr. Ambedkar warned would threaten democracy.
Table of Contents
Democratic Constitution In South Africa
Today, we’ll learn about Nelson Mandela – a hero who fought for fairness in South Africa. Imagine being jailed just for wanting equal rights! Let’s explore his powerful words.
Mandela dreamt of a world where everyone lives together equally, like all players in a cricket team getting the same chance to bat 🏏.
He hated both “white domination” (whites ruling over Blacks) and “black domination” (Blacks ruling over whites). He wanted true democracy instead!
📚 Key Ideas Explained
1. Fought against white and black domination
Mandela believed no race should control another. In India, this is like saying no community should bully others – everyone deserves respect!
2. Democratic and free society
He wanted a country where all people vote, speak freely, and share power – just like India’s democracy after 1947!
3. Harmony and equal opportunities
His dream: A united society (like a family sharing sweets 🍬) where everyone gets the same chances in school, jobs, and life.
4. Prepared to die for his ideal
Mandela showed ultimate sacrifice – like Bhagat Singh or Gandhi ji. He was ready to give his life for freedom!
5. Apartheid regime
This was South Africa’s cruel system separating Blacks and whites. Blacks couldn’t vote, use same buses, or schools as whites – just like untouchability in old India.
6. Sentenced to life imprisonment
For opposing apartheid, Mandela got 27 years in jail! His “crime”? Wanting equality.

📊 Mandela’s Struggle vs. Apartheid Reality
| Mandela’s Dream ☀️ | Apartheid Reality ☔️ |
|---|---|
| All races live together | Blacks & whites separated |
| Equal rights for all | Blacks had no voting rights |
| Peaceful democracy | Violence against protesters |
| Shared opportunities | Blacks paid less, had poor schools |
Example from India: Imagine if only rich kids could study in good schools 🎒 – that’s unequal opportunity, like apartheid!
❓ Check Your Understanding
Q1: Why did Mandela oppose both white AND black domination?
A: He wanted true equality – no group controlling another!
Q2: What does “prepared to die for his ideal” tell us about Mandela?
A: He was brave and committed – freedom mattered more than his life!
📝 Practice Questions (Based only on the text!)
🔹 MCQ
- Where was Mandela imprisoned for 27 years?
a) Delhi Jail
b) Robben Island
c) Mumbai Prison
d) Cape Town FortAnswer: b) Robben Island ✅ - What was Mandela’s “ideal”?
a) White rule in South Africa
b) A society with harmony and equal opportunities
c) Black domination over whites
d) Wealth for his familyAnswer: b) ✅
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): Mandela was sentenced to life imprisonment.
- Reason (R): He dared to oppose the apartheid regime.Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Talk to a friend:
If you saw someone being treated unfairly in school (like apartheid), what would YOU do? 🤔
✨ Mandela’s lesson: Stand up for justice, even if it’s hard!
Struggle against apartheid
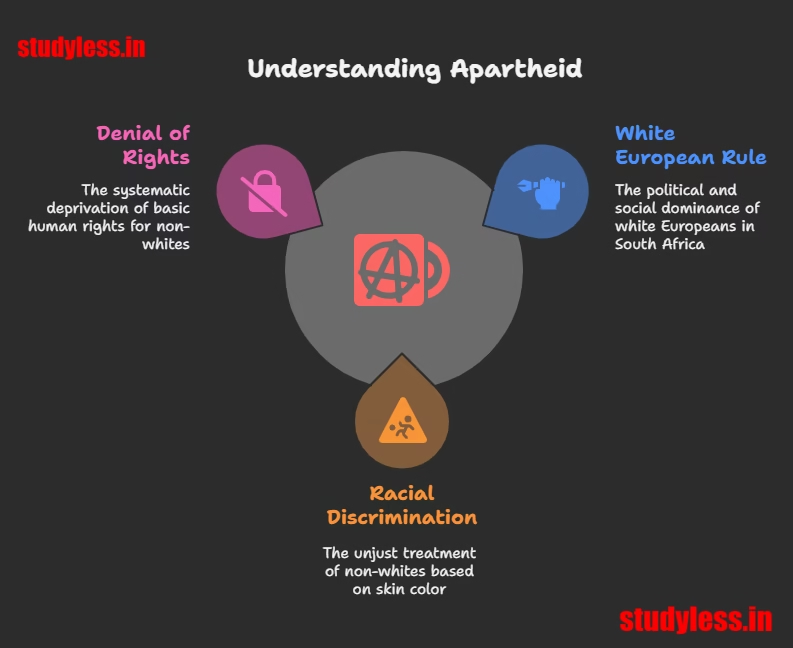
Apartheid – a cruel system of racial discrimination in South Africa. Imagine being banned from parks, schools, or buses just because of your skin color! Let’s dive in.
Apartheid was a brutal system where white Europeans ruled South Africa and treated non-whites as inferior. People were divided by skin color and denied basic rights – like a school where only “fair-skinned” kids can use the playground. The brave fight against this injustice was led by heroes like Nelson Mandela!
📚 Key Concepts Explained
1. Apartheid
- A racial discrimination system unique to South Africa.
- Imposed by white Europeans who settled there (like British rulers in India).
- Labeled people by skin color:
- Blacks (native, 75% population) ❌
- Whites (settlers, rulers) ✅
- Coloured (mixed race) ❌
- Indians (migrants) ❌
2. Segregation
- Total separation in public spaces:
- 🚌 Trains/buses, 🏥 Hospitals, 🏫 Schools, 🏖️ Beaches, 🚻 Toilets – all “whites only” or “non-whites only”.
- Blacks needed permits to work in white areas – like needing a “pass” to enter your own classroom!
3. Oppression
- Non-whites had no voting rights 🗳️.
- Blacks couldn’t live in white areas or form protest groups.
- Government detained, tortured, and killed protesters.
4. Struggle Against Apartheid
- Since 1950, blacks, coloured, and Indians united to fight back.
- African National Congress (ANC) led marches and strikes – like India’s freedom struggle!
- Sensitive whites joined too – proving humanity crosses color lines.
- .
📊 Apartheid vs. Resistance: A Snapshot
| Apartheid Rules ⚠️ | Resistance Actions ✊ |
|---|---|
| Skin-color labels (black/white/coloured/Indian) | ANC united all non-whites + white allies |
| No voting rights for non-whites | Protest marches and strikes |
| Segregation in public spaces | International criticism of apartheid |
| Violence against protesters | Heroes like Mandela sacrificed freedom |
Indian Example:
Imagine if only North Indians could vote 🔵, and South Indians were banned from malls 🔴 – that’s apartheid!

❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why was apartheid “unique”?
→ It legally divided people by skin color – no other country did this so harshly! - How was India’s occupation by Europe SIMILAR to South Africa?
→ Both were colonized by force – but in South Africa, whites stayed as rulers.
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (Based only on the text!)
- Who led the anti-apartheid struggle?
a) United Nations
b) African National Congress (ANC)
c) European Union
d) Red Cross
Answer: b) ANC ✅ - What did “segregation” mean under apartheid?
a) Mixing all races
b) Separate spaces for whites/non-whites
c) Equal schools for everyone
d) Voting rights for Indians
Answer: b) ✅
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): Blacks needed permits to work in white areas.
- Reason (R): Apartheid laws aimed to strictly separate races.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Think & Share
If your school practiced “segregation” – separating students by skin color or religion – how would you protest? 🙋♂️🙋♀️
✨ Key Lesson: Discrimination hurts everyone. True freedom means equality for ALL! 🌈
Towards a new constitution
South Africa’s New Dawn: Freedom & Forgiveness
Now let’s explore how South Africa turned from apartheid to democracy – a story of hope, unity, and one of the world’s finest constitutions!
After decades of brutal apartheid, whites and blacks chose peace over revenge. They built a new South Africa based on equality, forgiveness, and democracy – like rivals becoming teammates for a common goal! 🏆
📚 Key Concepts Explained
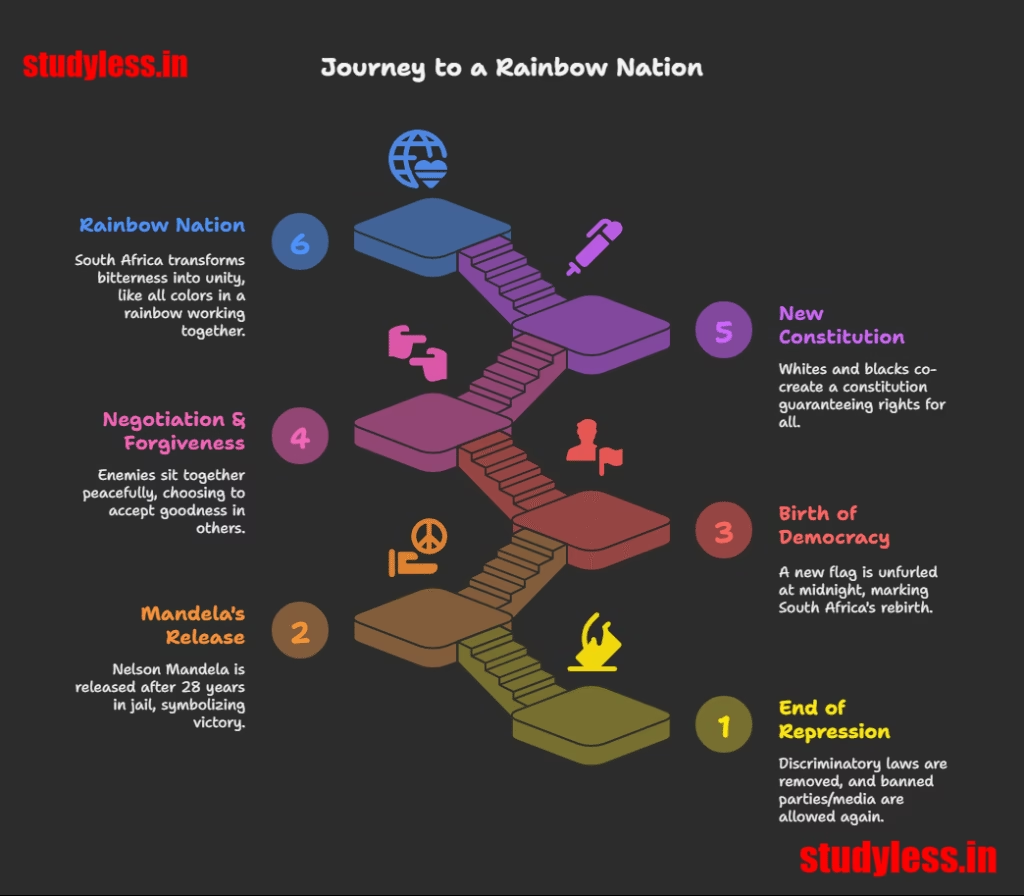
1. End of Repression
- The apartheid government realized it couldn’t control blacks through force anymore.
- Discriminatory laws were removed, and banned parties/media were allowed again.
2. Nelson Mandela’s Release
- After 28 years in jail, Mandela walked free! 🕊️
- Indian example: Like Bhagat Singh’s release (if it happened) – a symbol of victory!
3. Birth of Democracy (26 April 1994)
- New flag unfurled at midnight – marking South Africa’s rebirth!
- Fun fact: India’s “Tryst with Destiny” speech also happened at midnight! ⏰
4. Negotiation & Forgiveness
- Enemies sat together peacefully because they chose to “accept goodness in others” (Mandela’s words).
- Black leaders asked fellow blacks to forgive whites for past atrocities.
5. The New Constitution
- Whites (former oppressors) and blacks (freedom fighters) co-created it.
- It guarantees extensive rights for all, making it a global model.
- Preamble spirit: “Never repeat the past; build a shared future!”
6. Rainbow Nation
- South Africa transformed bitterness into unity – like all colors in a rainbow 🌈 working together!
📊 Apartheid vs. New South Africa
| Apartheid Past ☠️ | Democratic Future ✨ |
|---|---|
| Whites vs. Blacks | Multi-racial government |
| Violence & revenge | Forgiveness & unity |
| No rights for non-whites | World’s finest constitution |
| Segregation | “A country that belongs to ALL” (Mandela) |
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why did the apartheid government change its policies?
→ Because protests made repression impossible! - What is the “Rainbow Nation”?
→ A South Africa united in diversity – all races living together!
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (Based only on the text!)
- When was South Africa’s new flag unfurled?
a) 15 August 1947
b) 26 January 1950
c) 26 April 1994 ✅
d) 31 December 1999 - What did Mandela mean by “faith in goodness”?
a) Trusting enemies can change
b) Believing in magic
c) Hoping for wealth
d) Both a & c
Answer: a) ✅ (Key to peaceful transition!)
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): South Africa’s constitution is a global inspiration.
- Reason (R): It was born from enemies working together for equality.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Think Like a Leader
If you were Mandela, would you forgive those who jailed you? Why? 🤔
🌟 Mandela’s Lesson: “Your heart can be stronger than your scars.”
Why Do We Need A Constitution?
📜 Why We Need a Constitution: Lessons from South Africa
Time to understand constitutions – the rulebook of a nation. Let’s see why even bitter enemies like South Africa’s whites and blacks agreed to create one!
After apartheid, whites and blacks distrusted each other. A constitution was their peace treaty – a set of fixed rules to protect everyone’s rights and prevent future fights. Like a classroom contract signed by all students!
📚 Key Concepts Explained
1. Why South Africa Needed a Constitution
- Blacks feared whites would block majority rule.
- Whites feared blacks would seize their property.
- Solution: A compromise → Majority rule + Property protection for minorities.
2. What Constitutions Do
| Function | Example |
|---|---|
| Build Trust 🤝 | Rules ensure no group cheats (e.g., whites won’t lose property unfairly). |
| Define Power ⚖️ | Specifies how leaders are chosen (e.g., elections). |
| Limit Government 🚫 | Stops rulers from becoming dictators (e.g., can’t jail critics). |
| Protect Rights 🛡️ | Guarantees freedoms (speech, religion) for all citizens. |
| Express Dreams 🌈 | Pledges to build a fair society (e.g., South Africa’s “Rainbow Nation”). |
3. Constitution = Supreme Law
- No one is above it – not even the president!
- Guarantees stability: Rules can’t be changed easily (unlike regular laws).
4. Not Just for Democracies!
- All countries (even non-democracies) have constitutions.
- But only democracies use them to protect people’s rights.
- Example: India’s constitution (1950) vs. North Korea’s (exists but ignored).

🌍 Indian Connection
Imagine if after India’s freedom struggle:
- Hindus feared Muslims would dominate.
- Muslims feared Hindus would oppress them.
Solution? Our constitution banned discrimination and gave equal rights to all!
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why couldn’t South Africa just use “gentlemen’s agreement” instead of a constitution?
→ Because trust was broken! Written rules = guarantee no one cheats later. - How does a constitution protect minorities?
→ By limiting majority power (e.g., can’t seize property).
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (Based only on the text!)
- What is the MAIN role of a constitution?
a) To help leaders become rich
b) Build trust and coordination among citizens ✅
c) To promote one religion
d) Allow unlimited government power - Why did South African whites accept majority rule?
a) They loved black leaders
b) Blacks agreed to protect white property ✅
c) They wanted to leave the country
d) UN forced them
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): A constitution is essential for democracies.
- Reason (R): It defines how governments are formed and limits their power.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Think & Discuss
Your school club needs a constitution!
- What 3 rules would you include?
- How would it prevent fights between members?
✨ Remember: A constitution turns enemies into teammates – just like South Africa did! 🕊️
Making Of The Indian Constitution
Let’s explore how our Constitution was born during tough times – just like building a sandcastle in a storm! 🌪️🏰
India’s Constitution was crafted amid chaos – Partition violence, princely state disputes, and deep fears about the future. Yet, our leaders turned these challenges into a rulebook for unity!
📚 Key Challenges Explained
1. Partition Trauma
- Religious division split India-Pakistan in 1947.
- 10+ lakh people died in violence 💔.
- Example: Imagine your school splitting into two – friends suddenly becoming strangers.
2. Princely States Puzzle
- 565 princely states (like Hyderabad, Kashmir) had to choose:
- Join India 🇮🇳 or Pakistan 🇵🇰 or stay independent❓
- Sardar Patel “convinced” them to merge – like persuading friends to join your cricket team!
3. Uncertain Future
- Leaders felt anxious and insecure – no one knew if India would survive!
- Quote: “The future looked dark; we were writing rules for a newborn in a storm.”

📊 India’s Challenges vs. Achievements
| Problems (1947) ☁️ | Solutions (Constitution) ☀️ |
|---|---|
| Partition violence | Secularism: Equal respect to all religions ✨ |
| Princely states’ resistance | Federalism: States + Centre share power 🤝 |
| Fear of disintegration | Unity in Diversity: “India, that is Bharat” 🇮🇳 |
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why was “merging princely states” tricky?
→ Rulers wanted independence – Patel had to negotiate! - How did Partition affect constitution-making?
→ Leaders added rights to equality so no community felt unsafe agai
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (Strictly from the text!)
- What triggered the Partition of India?
a) Language differences
b) Religious differences ✅
c) Economic inequality
d) British conspiracy - Who decided if princely states joined India?
a) Citizens voted
b) Their rulers ✅
c) British Parliament
d) United Nations
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): Making India’s Constitution was difficult.
- Reason (R): India faced Partition violence and princely state challenges.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Imagine This!
If YOU were a leader in 1947:
- What one right would you add to the Constitution to heal Partition wounds?
- How would you convince a princely state to join India?
✨ Fun Fact: Our Constitution took 2 years, 11 months, 18 days – written with a golden pen! ✍️🇮🇳
🌟 Key Takeaways
| Lesson | Indian Example |
|---|---|
| Unity over Division | Constitution made India strong despite diversity 🌈 |
| Hope over Fear | Leaders turned anxiety into a vision of justice 👁️ |
| Peace over Conflict | Rights protected all – Hindus, Muslims, Sikhs, Christians 🕊️ |
“We made the Constitution not just for us, but for generations unborn.”
– Dr. B.R. Ambedkar (Architect of Indian Constitution)
Path To The Constitution
📜 India’s Constitutional Journey: From Struggle to Solution– Now, we’ll see how our freedom fighters turned dreams into rules – like building a LEGO castle with pieces from around the world! 🧱🌍
India had a huge advantage over South Africa: decades of freedom struggle had already created agreement on democracy’s core values. Our leaders didn’t start from scratch – they built on a strong foundation of shared ideals!
📚 Key Concepts Explained
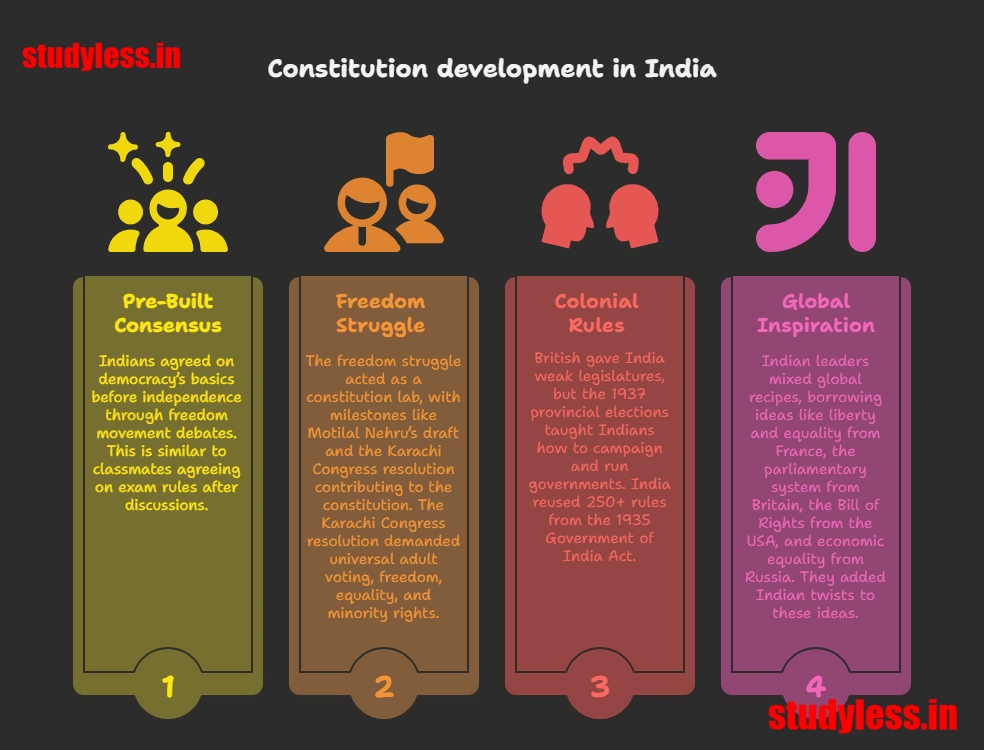
1. Pre-Built Consensus
- Unlike South Africa, Indians already agreed on democracy’s basics before independence.
- How? Through freedom movement debates – like classmates agreeing on exam rules after discussions!
2. Freedom Struggle = Constitution Lab
| Milestone | Contribution |
|---|---|
| 1928: Motilal Nehru’s draft | First Indian constitution blueprint 📜 |
| 1931: Karachi Congress resolution | Demanded universal adult voting, freedom, equality, and minority rights ✊ |
3. Learning from Colonial Rules
- British gave India weak legislatures (like toy parliaments 🧸).
- But! 1937 provincial elections taught Indians:
- How to campaign 🗣️
- How to run governments 🏛️
- Fun fact: We reused 250+ rules from the 1935 Government of India Act!
4. Global Inspiration, Indian Touch
Our leaders were like chefs 👨🍳 mixing global recipes:
| Country | Idea Borrowed | Indian Twist |
|---|---|---|
| France 🇫🇷 | Liberty, equality | Added fraternity (brotherhood) |
| Britain 🇬🇧 | Parliamentary system | Made it federal (Centre + States) |
| USA 🇺🇸 | Bill of Rights | Expanded to Fundamental Rights |
| Russia 🇷🇺 | Economic equality | Added Directive Principles |
Golden Rule: Never copied blindly! Always asked: “Will this work for India?” ✅
🌟 India’s Unique Advantage
| South Africa | India |
|---|---|
| Whites & blacks were enemies | All groups fought together against British |
| No shared vision before 1990 | 50+ years of freedom struggle consensus |
| Built constitution from zero | Reused colonial experience + global ideas |
Example: Like reusing your old project’s research for a new assignment – smart and efficient! 💡
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why was the 1937 election important for constitution-making?
→ It gave Indians practical experience in running legislatures! - How did Motilal Nehru’s 1928 draft help?
→ It proved Indians already agreed on voting rights/equality decades before freedom!
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (Strictly from the text!)
- What did the 1931 Karachi Resolution demand?
a) King as ruler
b) Universal adult franchise and minority rights ✅
c) Permanent British rule
d) Only Hindu voting rights - Which colonial law inspired India’s constitution?
a) Magna Carta
b) Government of India Act, 1935 ✅
c) US Constitution
d) French Civil Code
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): India didn’t copy other constitutions blindly.
- Reason (R): Leaders adapted foreign ideas to India’s needs.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Be a Constitution Maker!
If YOU were in the Constituent Assembly:
- Which one global idea would you add to our constitution?
- How would you make it uniquely Indian?
✨ Fun Fact: The final constitution had 395 articles – but every word was debated 3x! 🤯
Key Lesson: Great rules take time, teamwork, and trust! 🤝🇮🇳
The Constituent Assembly
📜 Meet India’s Constitution Makers: The Constituent Assembly –The incredible team that wrote India’s Constitution. Imagine 299 superheroes 🦸♂️🦸♀️ debating for 3 years to create our rulebook – let’s dive in!
The Constituent Assembly was India’s “Dream Team” – elected leaders who turned freedom dreams into our Constitution. Even today, we respect their work because they built broad consensus, represented all Indians, and debated every word with care!

📚 Key Concepts Explained
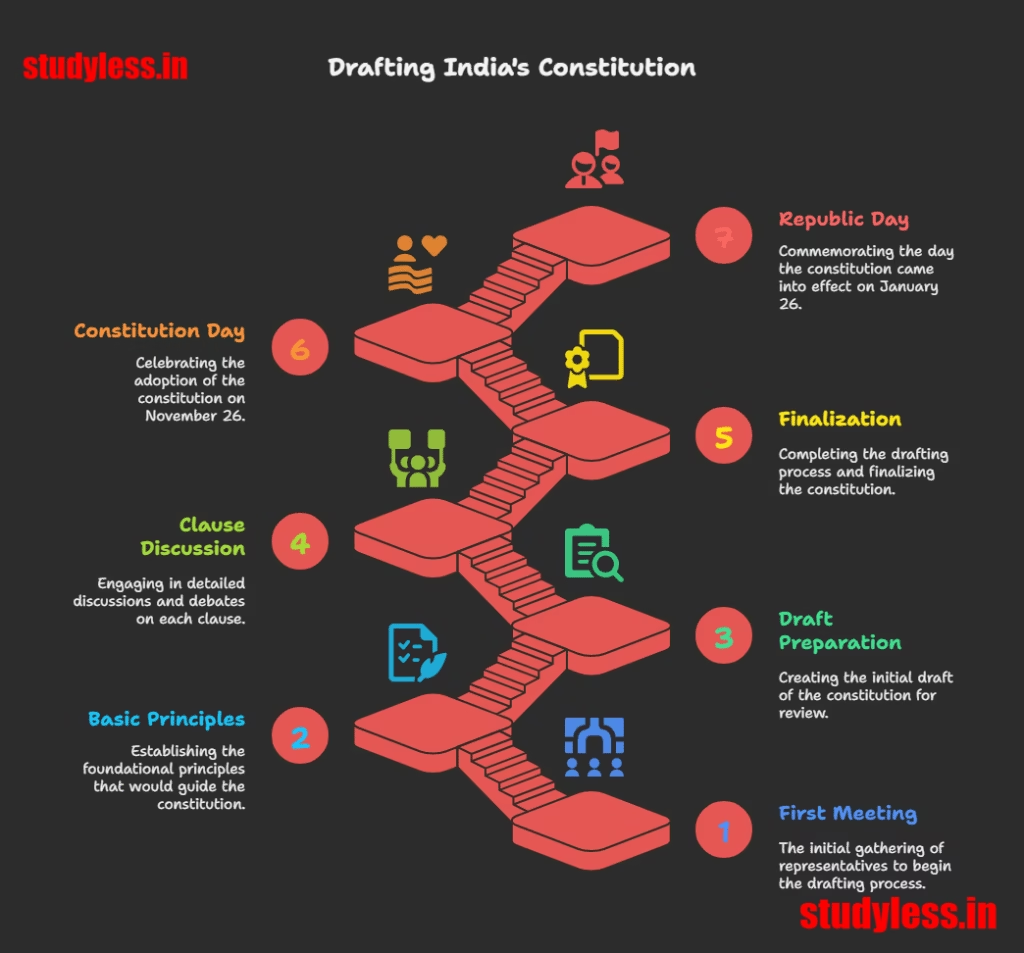
1. What was the Constituent Assembly?
- A group of 299 elected representatives who drafted India’s Constitution.
- First meeting: December 1946 (during Partition chaos!).
- Finalized Constitution: 26 November 1949 (celebrated as Constitution Day).
- Effective from: 26 January 1950 (Republic Day 🎉).
2. Why do we STILL accept this 70+ year-old Constitution?
| Reason | Simple Explanation |
|---|---|
| Broad Consensus 🤝 | Reflected agreements from freedom struggle (not personal opinions). |
| Represented All Indians 🌈 | Included diverse regions, religions, languages – like a mini-India! |
| Thorough & Transparent Process 🔍 | Debated 114 days, 2000+ amendments – every word preserved in 12 volumes! |
3. How was the Assembly elected?
- No universal adult franchise then → Members chosen by Provincial Legislatures (like state MLAs).
- Ensured fair regional representation: Punjab to Tamil Nadu, Hindus to Muslims, farmers to lawyers!
4. The Makers & Their Method
Chairman of Drafting Committee: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar (Father of Indian Constitution).
Work Style:
Step 1: Agree on basic principles.
Step 2: Draft prepared → Clause-by-clause discussion.
Step3: Recorded every debate (‘Constituent Assembly Debates’).
📊 Key Dates at a Glance
| Event | Date |
|---|---|
| Elections to Constituent Assembly | July 1946 |
| First Meeting | December 1946 |
| Constitution Adopted | 26 November 1949 |
| Constitution Effective | 26 January 1950 |
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why didn’t all Indians vote for the Constituent Assembly?
→ Because universal adult franchise didn’t exist then – only MLAs voted! - How did the Assembly ensure diverse voices?
→ By including leaders from all regions, castes, religions, and professions!
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (Strictly from the text!)
- When did India’s Constitution come into effect?
a) 15 August 1947
b) 26 January 1950 ✅
c) 26 November 1949
d) 30 January 1948 - Who chaired the Drafting Committee?
a) Jawaharlal Nehru
b) Mahatma Gandhi
c) Sardar Patel
d) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar ✅
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): The Constituent Assembly represented Indian diversity.
- Reason (R): It had members from all regions, religions, and social groups.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Be a Constitution Detective!
Imagine you find a page from the Constituent Assembly Debates:
- What one question would you ask Dr. Ambedkar?
- Why are these debates called the Constitution’s “user manual”?
✨ Fun Fact: The 12 volumes of debates are still used by judges to interpret the Constitution! 📚⚖️
🌟 Why This Assembly Rocks!
| Challenge | Their Genius Move |
|---|---|
| Partition chaos | Focused on unity and future 🕊️ |
| Diverse opinions | Debated, amended, compromised ✨ |
| No public vote | Still built a people-approved Constitution via consensus |
“The Constitution is not a mere lawyer’s document; it is a vehicle of life!”
– Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Guiding Values Of The Indian Constitution
📜 The Soul of Our Constitution: Dreams of Gandhi, Ambedkar & Nehru
Now it is the time to understand the heart of India’s Constitution. Let’s decode the big dreams that shaped our rulebook – through the words of three giants!
Our Constitution isn’t just rules – it’s a promise to build an India free from inequality, where every voice matters. The Preamble (intro) captures this philosophy!
📚 Three Visions, One Constitution
1. Mahatma Gandhi’s Dream (1931)
Though not in the Assembly, his vision inspired it!
“I want an India where…
- The poorest feel it’s THEIR country 🏡
- No high/low classes – all equal! ⚖️
- All communities live in harmony 🙏☪️✝️☬️
- No untouchability or drugs 🚫🍷
- Women equal to men 👩⚖️👨”
Indian Example: Like a village sabha where farmers, women, and youth all decide together!
2. Dr. Ambedkar’s Warning (1950)
Architect of the Constitution, but worried about contradictions:
“On 26 Jan 1950, we enter a life of contradictions:
- POLITICAL EQUALITY: One person, one vote ✅
- SOCIO-ECONOMIC INEQUALITY: Caste/wealth divide still exists! ❌
If we don’t fix this, democracy will collapse!“
Indian Example: A Dalit voter and a rich businessman both vote (= political equality), but the Dalit faces discrimination (= social inequality).
3. Jawaharlal Nehru’s Pledge (1947)
At midnight freedom speech:
“We made a tryst with destiny! Now, our responsibility:
- End poverty, ignorance, disease 💉📚🍽️
- Fight inequality ⚖️
- Work till no Indian suffers 😢→😊”
Indian Example: Like a school project where all students get equal resources to succeed!
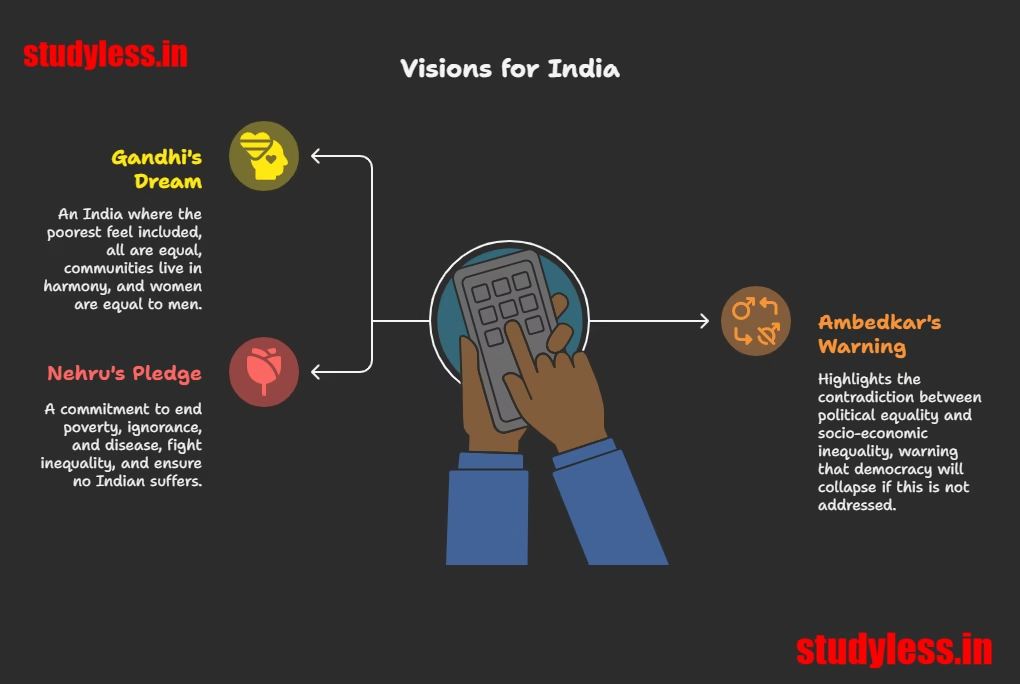
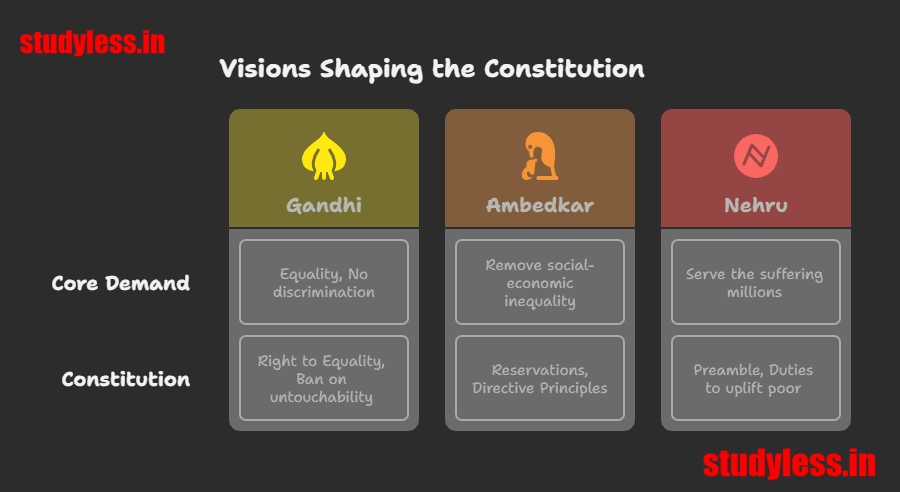
📊 How Their Visions Shaped the Constitution
| Leader | Core Demand | In the Constitution |
|---|---|---|
| Gandhi | Equality, No discrimination | Right to Equality (Art 14-18), Ban on untouchability (Art 17) |
| Ambedkar | Remove social-economic inequality | Reservations (Art 15-16), Directive Principles (Art 38-39) |
| Nehru | Serve the suffering millions | Preamble (“Justice, Liberty, Equality”), Duties to uplift poor |
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why wasn’t Gandhi in the Constituent Assembly?
→ He chose not to join, but his ideas guided it! - What “contradiction” did Ambedkar fear?
→ Voting equality vs. real-life inequality (caste/class).
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (From the text!)
- What did Gandhi want to eliminate from India?
a) Schools
b) Untouchability and drugs ✅
c) Voting rights
d) Cities - Nehru’s “tryst with destiny” speech marked:
a) End of World War
b) India’s freedom at midnight ✅
c) First election
d) Constitution draft
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): Ambedkar worried about India’s future.
- Reason (R): He saw equality in voting but not in society.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💬 Think Like a Leader!
Whose vision speaks to YOU the most?
- Gandhi’s harmony?
- Ambedkar’s equality?
- Nehru’s service?
✨ Preamble is the KEY!
“WE, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA… secure to all citizens:*
JUSTICE (social, economic, political),
LIBERTY (thought, expression, faith),
EQUALITY (status, opportunity),
FRATERNITY (brotherhood)!”*
🌟 Your Takeaway Table
| Concept | Simple Meaning |
|---|---|
| Gandhi’s Dream | An India where no one feels left out 🌈 |
| Ambedkar’s Warning | Voting rights aren’t enough – fight real inequality! ⚠️ |
| Nehru’s Tryst | Freedom = Responsibility to lift others up! 🔼 |
“Constitution isn’t a lawyer’s document – it’s a promise of hope!”
– Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Philosophy Of The Constitution
📜 The Heart & Machinery of India’s Constitution -The soul (Preamble) and structure (institutions) of our Constitution.
Let’s dive in!
Our Constitution is like a Banyan Tree 🌳:
- Roots = Preamble (values from freedom struggle)
- Branches = Institutions (systems to make values real)
🌟 Part 1: The SOUL – Preamble
(The “Poem of Democracy” that guides everything!)
📜 Preamble Keywords Explained
| Word | Meaning | Indian Example |
|---|---|---|
| WE, THE PEOPLE | Power belongs to all Indians | Like a panchayat where villagers decide together! |
| SOVEREIGN | India is master of its own destiny | No foreign power can boss us (like 1947!) |
| SOCIALIST | Wealth shared fairly with all | Free mid-day meals in govt schools 🥘 |
| SECULAR | All religions equal before law | Diwali, Eid, Christmas all holidays! 🪔🕌🎄 |
| DEMOCRATIC | People rule through elections | Voting for class monitor = mini-election! 🗳️ |
| REPUBLIC | No king! Leaders elected by us | President elected, not born like a Maharaja |
| JUSTICE | Fairness in society, economy, law | Reservations for SC/ST/OBC students ✊ |
| LIBERTY | Freedom to think, speak, worship | Right to protest peacefully! 📢 |
| EQUALITY | All equal regardless of caste/wealth | No “whites-only” benches like apartheid! ♿ |
| FRATERNITY | Brotherhood among all Indians | “Unity in Diversity” slogan 🤝 |
✨ Fun Fact: The Preamble is like a filter – any law against these values is UNCONSTITUTIONAL! ⚖️

⚙️ Part 2: The MACHINERY – Institutional Design
(How values become reality!)
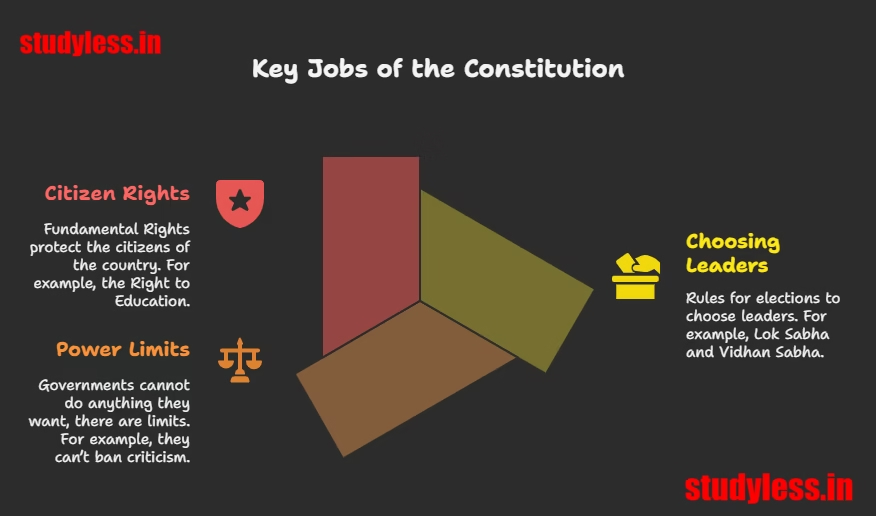
🔧 3 Key Jobs of the Constitution
- Choosing Leaders: Rules for elections (Lok Sabha, Vidhan Sabha).
- Power Limits: Govts can’t do anything they want! (e.g., can’t ban criticism).
- Citizen Rights: Fundamental Rights protect YOU! (e.g., Right to Education).
🔄 Why Amendments?
- Our Constitution is living – it grows with society!
- Example:
- 1950: No mention of education rights.
- 2002: 86th Amendment → Added Right to Education (Art 21A)!
- Like updating your phone 📱 – new features for new needs!
📏 Institutional Design Explained
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Detailed Rules | 395 Articles! Covers everything from PM’s powers to panchayat funds. |
| Flexibility | Can be amended (changed) – 104 times so far! |
| Legal Language | Precise wording to avoid confusion (like a science lab manual!). |
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why is the Preamble called the Constitution’s “soul”?
→ It holds the core values that judge every law! - How is “secularism” practiced in India?
→ Govt doesn’t favor any religion – all treated equally!
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (From the text!)
- What does “REPUBLIC” in the Preamble mean?
a) Rule by a king
b) Rule by elected leaders ✅
c) Rule by the army
d) Rule by foreigners - Why can the Constitution be amended?
a) To please politicians
b) To adapt to changing society ✅
c) To copy other countries
d) To make it shorter
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): The Constitution limits government power.
- Reason (R): It provides Fundamental Rights to citizens.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💡 Activity: Be a Preamble Artist!
Redesign the Preamble as an emoji story:
Example:
WE 👨👩👧👦, THE PEOPLE OF INDIA 🇮🇳, having solemnly resolved…
Your Turn! ➡️
✨ Constitution Fun Fact: The original Preamble was written by Beohar Rammanohar Sinha – an artist! 🖌️
🌈 Your Takeaway Table
| Concept | Real-Life Impact |
|---|---|
| Preamble Values | Guides laws – e.g., banned untouchability (Art 17) |
| Institutional Design | Creates systems – e.g., Election Commission conducts polls! |
| Amendability | Keeps Constitution alive – e.g., added privacy rights in 2017! |
“The Constitution is not a museum exhibit but a living force!”
– Justice Bhagwati
Institutional Design: Turning Values into Working Systems
Our Constitution is like a nation-building toolkit 🔧:
It takes the dreams in the Preamble and builds real institutions (Parliament, Courts) to make them come true!
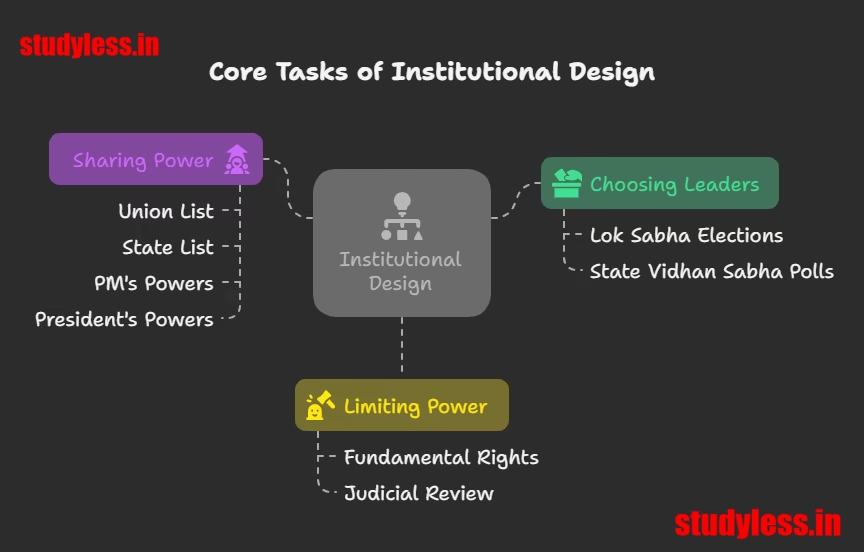
📋 3 Core Tasks of the Institutional Design
(As described in your text)
| Task | What It Means | Example from Constitution |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Choosing Leaders 🗳️ | Rules for electing governments | – Lok Sabha elections every 5 years (Art 83) – State Vidhan Sabha polls |
| 2. Sharing Power ⚖️ | Who decides what? | – Centre (Union List) vs. States (State List) (7th Schedule) – PM’s powers (Art 74) vs. President’s (Art 53) |
| 3. Limiting Power 🛑 | Protecting citizens from misuse of power | – Fundamental Rights (Art 14-32) – Courts can strike down unconstitutional laws |
🔄 Why Does the Constitution Need Updates?
(Hint: It’s a LIVING document!)
| Feature | Reason | Real-Life Example |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed & Long 📜 | Covers complex governance needs | 395 Articles, 12 Schedules! |
| Amendments ✏️ | Adapts to changing society | 104 amendments so far! (e.g., Right to Education added in 2002) |
| Not Sacred/Static 🚫 | Responds to people’s aspirations | GST (2017) required constitutional change |
✨ Fun Fact: The Constitution has its own “update rules” (Art 368). Like a game that lets you add new levels! 🎮
🧠 Key Concepts Explained
1. “Legal Language is Tough, But Logic is Simple!”
- Yes, the Constitution uses precise terms (like a science textbook), but its core design is easy:
- Power comes from PEOPLE → Given to leaders via elections → Limited by citizens’ rights.
2. Why These 3 Tasks Matter Most
- Imagine a school:
- Choosing Leaders = Electing monitors 👨💼
- Sharing Power = Prefects (library) vs. Captains (sports) 🏀📚
- Limiting Power = Teachers can’t cancel holidays! 🚫📅
3. What’s NOT Covered This Year?
(But coming next year!)
- Salient Features like:
- Federalism (Centre-State balance) ⚖️
- Judiciary structure (Supreme Court/High Courts) ⚖️
- Local governments (Panchayats/Municipalities) 🏘️
❓ Check Your Understanding
- Why can’t the PM do whatever he wants?
→ Because the Constitution limits his power using Fundamental Rights! - How is India’s Constitution like a mobile app?
→ Both get regular updates (amendments) for better performance!
📝 Practice Questions
🔹 MCQ (Strictly from the text!)
- What is the purpose of constitutional amendments?
a) To make the Constitution longer
b) To keep it updated with society’s changes ✅
c) To please foreign countries
d) To remove fundamental rights - What protects citizens from government misuse of power?
a) School teachers
b) Fundamental Rights in the Constitution ✅
c) The Prime Minister
d) State governments
🔹 Assertion & Reason
- Assertion (A): The Indian Constitution is very detailed.
- Reason (R): It needs to cover complex governance arrangements.
Answer: Both A and R are true ✅, and R explains A.
💡 Activity: Build Your Mini-Constitution!
Create rules for your class:
- Choosing Leaders: How will monitors be elected?
- Sharing Power: What can monitors decide vs. teachers?
- Limiting Power: What’s off-limits? (e.g., “No cancelling PT period!”)
✨ Real-Life Connect:
When courts use the Constitution to cancel a law (like Section 377), that’s Task 3 in action! ⚖️🌈
🌟 Takeaway Summary
| Concept | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Choosing Leaders | Ensures WE THE PEOPLE control the government |
| Sharing Power | Prevents dictatorship – power divided fairly |
| Limiting Power | Rights protect you from unfair authorities |
| Amendments | Keeps the Constitution alive and relevant |
“Institutions turn ideals into reality – rights on paper become rights in life!” 🏛️💡
Wrapping It Up Constitutional Design Class 9: India’s Constitution Made Simple
Imagine India’s Constitution as your ultimate rulebook – created by the people, for the people!

Here’s why it matters to YOU
- Your Voice Matters
- Like electing class monitors 🗳️, the Constitution ensures YOU choose leaders through votes.
- Power Has Limits
- Leaders can’t do anything they want ❌ – your rights (like free speech or privacy) act as a shield!
- It Grows With You
- Just like apps get updates 📲, the Constitution changes with society (e.g., added education as a right in 2002).
Every time you…
- Speak your mind online,
- Celebrate any festival, or
- Demand fair treatment…
…that’s the Constitution working for YOU!
Keep questioning, keep learning – because this rulebook belongs to YOU! 🇮🇳✨
P.S. Next time you see the national flag, remember: the Constitution makes those colors stand for HOPE, not just cloth.
FAQs Constitutional Design Class 9
| 1.What is the constitutional design? | “A constitution is mainly about embodying [democratic] values into institutional arrangements” – defining how leaders are chosen, powers shared, and citizen rights protected. |
| 2.What is the main point of constitutional design? | To turn ideals into working systems: 1. Choose leaders via elections 2. Distribute decision-making power 3. Limit government with citizen rights. |
| 3.What are institutional design class 9 notes? | The framework for: – Choosing leaders (e.g., elections) – Power distribution (e.g., Centre vs. States) – Limits on power (e.g., Fundamental Rights). |
| 4.Why learn constitutional design? | To understand: – How values (Preamble) become laws – How institutions (Parliament, Courts) function – How citizens’ rights are safeguarded. |
| 5.When was our constitution designed? | Adopted: 26 November 1949 Effective: 26 January 1950. |
| 6.What is a constitution class 9? | “A set of written rules accepted by all people living in a country” – India’s has 395 articles defining governance and rights. |
| 7.Do we need a constitution? | Yes, to: – Build trust among diverse groups – Prevent abuse of power – Protect minority interests (e.g., South Africa protected white property rights). |
| 8.What is Constituent Assembly class 9? | “299 elected representatives” (1946-49) who drafted India’s Constitution through 114 days of debates, chaired by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar. |
| 9.What are constitutional rights? | Fundamental Rights in the Constitution that: – Cannot be violated by the government – Include equality (Art 14-18), freedom (Art 19), and protection against exploitation (Art 23-24). |
NCERT Book Chapter pdf – Constitutional Design
- New Mathematics Syllabus For Class 9 From 2026 – 20207 Session, Huge Changes Made!
- [2026-27] Class 9 New Social Science Syllabus By NCERT, Huge Changes
- Class 9 Science New CBSE Syllabus By NCERT From 2026 Onwards
- Structure Of Atom MCQs Class 9 Topic Wise In Quiz Format
- Structure Of Atoms Short Notes Class 9, Easy To Memorise!








Leave a Comment